In today's digital world, accessing media is easy, but often controlled by Digital Rights Management (DRM). DRM protects content creators' and distributors' rights by preventing unauthorized copying and distribution of digital content like movies, shows, and music. It uses encryption, requiring licenses or keys for authorized access. The Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) provides legal enforcement for these protections.

While DRM protects content, legitimate users may want to remove it. Common reasons include creating personal backups, ensuring device compatibility (playing content on devices not supported by the streaming service), and enabling offline viewing without a constant internet connection. In this guide, we'll explore the intricacies of DRM, the legal landscape surrounding its removal, and practical solutions for bypassing DRM protection, enable you to enjoy your favorite content offline, without restrictions.
Part 1. Why Remove DRM Protection? Legitimate Use Cases

Bought it, but can't watch it where you want? DRM, while protecting creators, often limits your rights as a consumer. This section explores legitimate reasons for DRM removal.
Personal Backups
Digital ownership is complicated by DRM restrictions. Users often want to create backups of legally obtained media to ensure long-term access, especially if the original platform ceases operations or alters its content offerings.
Device Compatibility
Different DRM technologies and platform-specific implementations can cause compatibility issues. Users may wish to play purchased content on devices not supported by the original streaming service or its particular DRM system, avoiding confinement to specific hardware or software ecosystems.
Offline Viewing
Many users want to enjoy downloaded content during travel or in locations with unreliable internet access. While some streaming platforms offer official download options, these often come with limitations including expiration dates and restrictions on the number of devices that can store the content.
Part 2. The Common Technology Behind DRM Systems
Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems protect digital content. Different systems exist, each with unique features and uses. Knowing these systems helps understand DRM removal.
Key DRM Systems:
- Widevine (Google): Common on Android devices and in Chrome/Firefox browsers. Uses a tiered security system (L1, L2, L3) based on device hardware, balancing protection with compatibility. Often uses MPEG-DASH and Common Encryption (CENC).
- PlayReady (Microsoft): Primarily for Windows and Microsoft Edge. Also supports CENC and MPEG-DASH. Includes features like playback tracking (metering) and security breach response. Tightly integrated with the Windows environment.
- FairPlay (Apple): Apple's system, used on macOS, iOS, tvOS, and Safari. Uses SAMPLE-AES encryption and HTTP Live Streaming (HLS). Focuses on secure communication and device-based decryption within the Apple ecosystem.
Multi-DRM: Because of the variety of devices, content providers often use Multi-DRM, protecting content with multiple DRM systems (Widevine, PlayReady, and FairPlay, for example) to ensure broad compatibility. This involves encrypting content multiple times and managing separate licenses for each DRM system.
Summary Table:
| DRM System | Developer | Main Platforms/Browsers | Encryption | Key Features | Security Levels |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Widevine | Android, Chrome, Firefox | CENC | Multi-level security, adaptive streaming | L1, L2, L3 | |
| PlayReady | Microsoft | Windows, Edge | CENC | Metering, breach response | N/A |
| FairPlay | Apple | macOS, iOS, tvOS, Safari | SAMPLE-AES | Secure communication, device-based decryption | N/A |
Part 3. Legal Considerations of DRM Removal

In the United States, the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) makes bypassing DRM protections illegal, with potential civil and criminal penalties. This applies even if you've legally purchased the content.
Laws differ internationally, with some countries allowing DRM removal for personal use or device compatibility. Fair use exceptions that typically permit limited use of copyrighted material for education, criticism, or research may not apply when DRM is involved.
The most important distinction is between personal use and distribution. While some users consider removing DRM for private use of legally purchased content ethically acceptable, sharing or distributing this content is generally illegal copyright infringement in most jurisdictions.
Part 4. General Methods to Break DRM Protection
Ready to remove DRM? The right method depends on the type of content. This section provides an overview of common techniques and tools used to bypass DRM on eBooks, DVDs/Blu-rays, and streaming video.
For eBooks
A common approach is to use software like Calibre, frequently paired with plugins such as DeDRM. These tools target popular eBook formats (e.g., Kindle, Kobo). The process might involve installing older versions of reading applications (like Kindle for PC/Mac) to ensure compatibility.
For DVDs and Blu-rays
Users often rely on specialized ripping software to bypass protections like CSS (Content Scrambling System) and regional coding. Free options like Handbrake (when combined with the libdvdcss library) can handle basic DVD DRM, but more sophisticated DRM schemes often require commercial software.
For Streaming Video
A simple, albeit less effective, method is screen recording. However, this often leads to reduced video quality and may fail to bypass all DRM (potentially resulting in black screen recordings). A more reliable solution is to use dedicated DRM removal software. These tools are typically designed for specific streaming services and allow for high-quality, DRM-free downloads.
Part 5. How to Bypass DRM Protection of Netflix
Netflix protects its content with sophisticated DRM systems like Widevine, effectively preventing conventional downloading methods. While Netflix offers an official download feature, it comes with significant limitations: downloads are restricted to specific devices (mainly smartphones and tablets), limits exist on downloadable titles per device, and downloaded content expires after a set period.
In response to these restrictions, StreamUlt Netflix Video Downloader provides a comprehensive solution for accessing Netflix content offline. This specialized software bypasses Netflix DRM protection, allowing users to download movies and shows directly to their computers in high quality.
StreamUlt delivers high-definition downloads (up to 1080p), saves content in universally compatible formats (MP4/MKV), preserves all audio tracks and subtitles in multiple languages, and enables efficient batch downloading of entire seasons. Additional features include Dolby 5.1 audio support, automatic metadata retention, and hardware acceleration for faster processing—all designed to provide a premium offline viewing experience without DRM restrictions.
How to Use StreamUlt Netflix Video Downloader
Step 1 Download and Install StreamUlt Netflix Video Downloader
Download the StreamUlt Netflix Video Downloader for your operating system (Windows or macOS) with the button above, then launch it on your computer.
Step 2 Log in to Netflix Account
You will be prompted to log in to your Netflix account through the software's built-in Netflix web player. Enter your credentials to access your Netflix library.
Step 3 Locate Target Videos
Navigate through the Netflix interface within StreamUlt to find the movies or TV shows you wish to download. You can use the search bar to quickly locate specific titles.
Step 4 Set Downloading Preferences
Once you have found the desired content, click on the download button associated with it. A pop-up window will appear, allowing you to customize your download settings. Here, you can choose the video quality (e.g., 1080p, 720p), select the output format (MP4 or MKV), and choose your preferred audio tracks and subtitle languages.
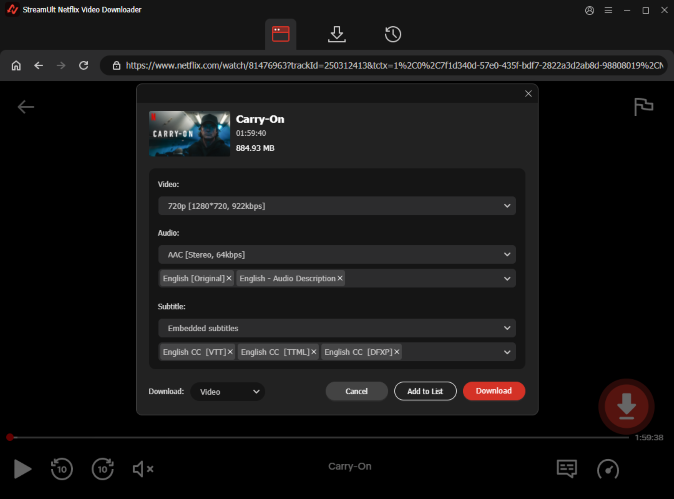
Step 5 Download the Video
After configuring your desired settings, click the "Download" button. StreamUlt will begin the process of removing DRM protection and downloading the selected Netflix video to your computer.

Once the download is complete, you can find the DRM-free video files in the designated output folder on your computer.
Part 6. Conclusion
In conclusion, navigating the world of DRM involves balancing the rights of content creators with the desires of consumers for flexibility. While DRM is a legal and technological necessity for protecting digital media, legitimate use cases, such as creating personal backups, ensuring device compatibility, and enabling offline viewing, often necessitate its removal.
Understanding the different DRM systems, the legal implications of circumventing them, and the available tools, like StreamUlt for Netflix, empowers users to make informed decisions about how they access and enjoy their legally purchased content. Ultimately, the choice rests with the individual, weighing the benefits of unrestricted access against the potential legal and ethical considerations.




Leave a Comment (0)